Dysphagia is the medical term used to describe difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia most often occurs secondary to a medical conditions such as a stroke, head and neck cancer, Parkinson disease, dementia, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), surgery, brain injury, or other illnesses, yet may also occur independent of any other medical diagnosis.
Speech-language pathologists are uniquely qualified to evaluate and treat disorders of swallowing as they have extensive education and knowledge of the anatomy, physiology, and functional aspects of the upper aerodigestive tract.
An individual may seek a swallowing evaluation if they are experiencing:
- Difficulty swallowing all or certain types of solid foods or liquids
- Swallowing discomfort
- Difficulty chewing
- Coughing or choking on saliva or when eating or drinking
- Recurrent pneumonia
Experts at NUCASLL provide evaluation and treatment for individuals experiencing dysphagia.
Services offered include:
- Outpatient clinical swallowing evaluations
- Outpatient swallowing therapy
NUCASLL patients may be referred for instrumental evaluation of swallowing, such as a modified barium swallow study (MBS) or Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) examination following the clinical exam. These examinations have different purposes and are complementary. Selection will be based on several factors such as the patient’s presentation and the nature of the disorder.
NUCASLL speech pathologists work closely with Northwestern’s Swallowing Cross System Collaborative Laboratory directed by Dr. Bonnie Martin-Harris.
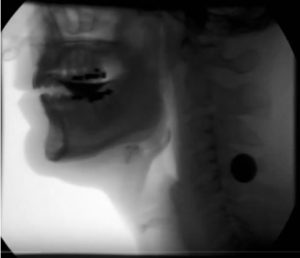
Modified Barium Swallow (MBS) Study
A MBS study is a digitally recorded motion x-ray of swallowing movements used to identify the type and severity of the swallowing disorder and to guide the appropriate type of swallowing treatment. The exam includes swallowing a standardized set of liquid and food consistencies to determine if and what liquids and foods can be safely and effectively.
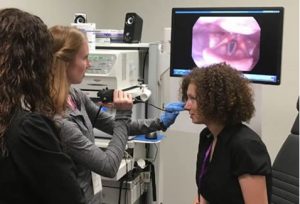
FEES Exam
A Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) procedure involves passage of a flexible endoscopic tube that houses a tiny camera through the nose and into the throat to evaluate swallow function The patient is given a variety of foods and liquids while the clinician directly observes movements of the swallowing structures.